Bullying in an Online World
The Facts of Cyberbullying
Bridgewater, Va.- Cyberbullying is an issue that many individuals face on a daily basis. Cyberbullying is specifically bullying that happens through digital devices like cell phones, computers and tablets, according to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
Online bullying also includes things like sending, posting, or sharing negative, harmful, false or mean content about someone else, and sharing personal or private information about someone else causing embarrassment or humiliation. Some cyberbullying can even cross the line into unlawful or criminal behavior.
State and local lawmakers have taken action to prevent bullying and protect children. However, these state laws generally do not prescribe specific consequences for kids who engage in bullying behavior and very few classify bullying as a criminal offense.
The Number of Those Being Bullied
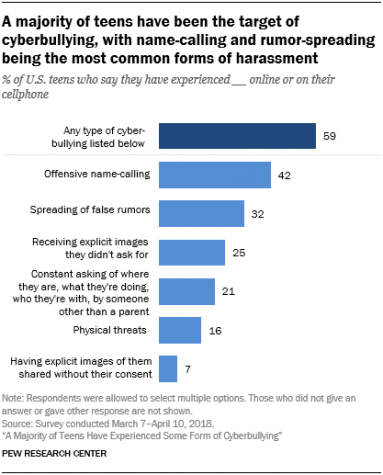
According to the Pew Research Center, 59% of U.S. teens have been bullied or harassed online, and a similar share say it is a major problem for people their age. At the same time, teens mostly think teachers, social media companies and politicians are failing at addressing this issue.
Pew Research Center asked young people to rate how key groups like school officials, tech companies and lawmakers are responding to cyberbullying and found that teens generally are critical of the way this problem is being addressed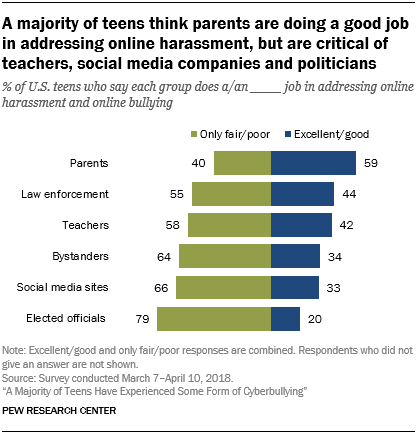
College Students
While there is a lot of information and studies regarding how cyberbullying affects teenagers and youth, there is little information about how it directly affects college students.
A study conducted in 2012 focusing on how cyberbullying affected females from four universities in the United States was published by the journal of Cyberpsychology, Behavior and Social Networking.
The study investigated the relationship between involvement in cyberbullying and depression or problem alcohol use among college females. Results indicated that 27% of participants had experienced cyberbullying in college; 17.4% of participants met the criteria for depression and 37.5% met the criteria for problem drinking.
When investigating associations between cyberbullying and depression, results demonstrated that participants who had experienced cyberbullying in any way — as a bully, victim or someone who has been both — had almost three times the odds of meeting clinical criteria for depression compared to those with no cyberbullying experience.
When looking at alcohol use, participants who experienced cyberbullying as a bully had increased odds of meeting the criteria for problem alcohol use compared to those with no cyberbullying experience. For victims, there were no significant associations with problem alcohol use compared to those with no cyberbullying experience.
When cyberbullying happens, experts recommend documenting, and keeping the evidence for purposes of reporting the behavior so that it can be addressed. Never respond to or forward cyberbullying messages and block the person who is cyberbullying.
Cyberbullying often violates the terms of service established by social media sites and internet service providers. If this occurs, review their terms and conditions or rights and responsibilities sections. Then report cyberbullying to the social media site so they can take action against users that are abusing the terms of service.
Cyberbullying is a serious issue that has touched many individuals and can have negative effects on the lives of all those affected by it.